The decentralized finance market (DeFi) has emerged as a result of the price crash in the cryptocurrency market in 2018. Then traders started borrowing one kind of cryptocurrency against another to escape losses, while holders lent them their coins to receive passive income, even though a small one.
The young market is yet to mature in contrast to the traditional lending market. However, its rate of growth, speed when introducing innovations, and potential for infrastructure development are worth paying attention to. Monthly launch of dozens of new services also contributes to its distribution.
In 2024, open-source projects started growing in popularity. Blockchain developers create traditional banking tools in a transparent decentralized architecture. With the help of smart contracts, they make the world of finances more accessible, free, and open.
Table of Contents
What decentralized finance is
DeFi is a decentralized public trustless ecosystem of financial services, protocols, and applications operating on public blockchains. It contains such familiar financial services as lending, insurance, asset management, and liquidity provision — the only difference is that everything is decentralized and mainly uses cryptocurrencies.
If Bitcoin is a decentralized system of digital currency, then DeFi is a decentralized system of financial instruments. Just like anyone can start using bitcoin by getting a wallet (BTC address), anyone can borrow and lend money or manage crypto assets through dApps and P2P apps.
The DeFi ecosystem provides all participants with access to traditional financial services by eliminating intermediaries and entry barriers. Primarily, DeFi services and applications were deemed useful in countries with underdeveloped and unstable economies. Then they also found demand in developed countries, especially in terms of lending and investing.
How decentralized finance works
DeFi works and attracts participants due to the following 7 principles:
- Decentralization. There are no central authorities, and operation rules are indicated in a smart contract. Once launched, an application can run autonomously.
- Self-governing. Participants govern projects through voting. Developers introduce changes and updates in protocols only if the latter collect the majority of votes.
- Transparency. Transactions are public and simultaneously pseudonymous. The majority of applications are open source, allowing independent experts to audit a smart contract to check its functionality and identify bugs.
- Cross-border factor. Services and applications are available to any Internet user.
- UI/UX flexibility. If a user doesn’t like an application’s interface, they can change it to an external one or create their own. Here, smart contracts are similar to open APIs.
- Inclusivity. Anybody can use a turnkey application or create their own. There are no regulators or accounts that require filling out forms or permissions in order to work with them. Users interact directly with smart contracts.
- Interoperability. New applications can be created by combining other turnkey DeFi products: stablecoins, DEXs, marketplaces, and prediction markets. So it is possible to create a custom structure using various combinations.
These principles are considered to be the benefits of DeFi in contrast to how the traditional financial sector operates.
What the features of the crypto lending market are
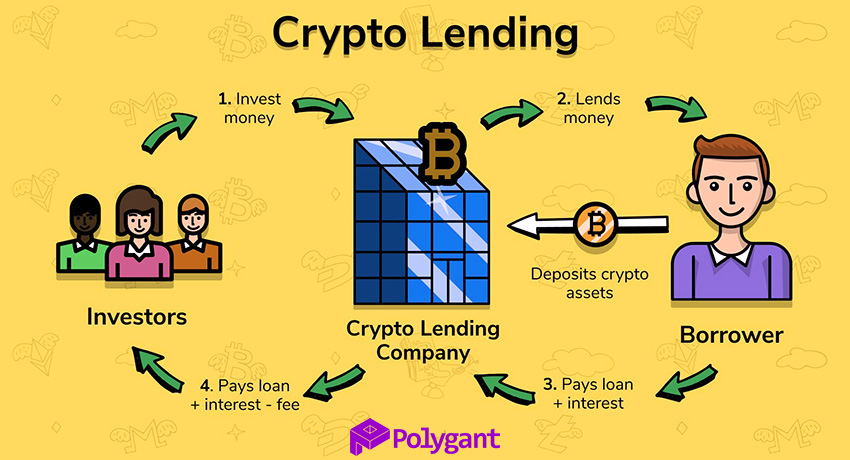
Cryptocurrency lending has two main parties: those who take out loans secured by digital assets, and those who lend them their assets. Often, there is a third party—services, platforms, protocols, and applications—used by the parties to settle transactions.
In centralized services, the main collateral is bitcoin, while in decentralized it is ether. However, nobody restricts participants to these extra popular cryptocurrencies. At the DeFi lending market, almost any assets are lent and borrowed against any collateral:
- Stablecoins and fiat currencies collateralised by cryptocurrencies. In cases with fiat currencies, the loan is transferred to the bank account of the borrower who needed to make up for the liquidity shortfall.
- Cryptocurrencies collateralised by native tokens on centralised platforms.
- Derivatives for trading on decentralised platforms.
- Cryptocurrencies collateralised by other digital currencies and assets. Deals are usually conducted through noncustodial lending protocols.
- ERC tokens collateralised by ether or stablecoins on Ethereum.
As you can see, centralized participants are also present in the DeFi lending market. On the one hand, this violates the primary principle — decentralization, which worries blockchain enthusiasts a great deal. On the other hand, lenders and borrowers are not bothered by the decentralization degree of their deals — they care more about the interest benefit.
If you want to create a DeFi app, don’t worry about a possible participation of something not truly decentralized, for example, an API from a centralized service or a stablecoin from an issuer such as Tether. In an app, interest rates are more important, as well as the convenience of UI and UX.
Try to provide your app with easy access to low-cost loans. Then it will be interesting to many residents of countries with banking systems that offer loans only at horrendous interest and with hidden fees accompanied by bureaucratic hurdles.