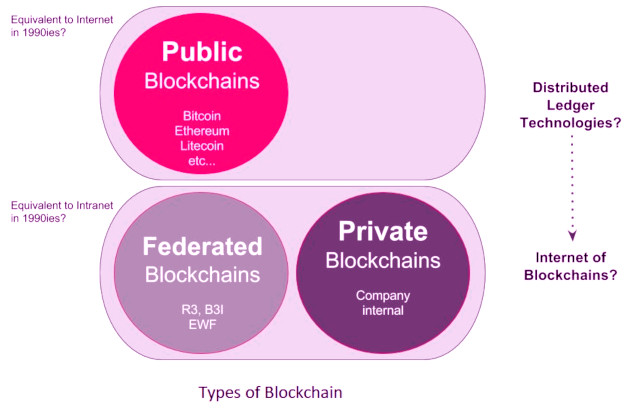
When we talk about blockchain technology, we need to distinguish between public blockchains and distributed ledger technology. Each of these technologies has completely different models of financing and investment, although both of them are based on similar fundamental blockchain principles.
Public blockchain technology has been made famous and funded by cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Zcash. On the other hand, private blockchains are mainly financed by consortia of companies, especially in the financial and banking sectors, as well as venture capital. According to the World Economic Forum, 80% of banks are working on projects related to blockchains. In this article, giving an overview of the future capabilities of blockchain technology, we will talk about the most important aspects of the investment level of private blockchains.
Table of Contents
The financial sector looks to the future
Private blockchains are being invested in mainly by companies in the financial and banking sectors. But other businesses are also exploring the opportunities offered by this technology. Although their investments have not reached the level accumulated in the financial sector.
Today, this sector is best suited to utilise blockchains. Recent years have seen a fintech boom, and banks have been forced to invest in new technologies to protect the traditional business model from a glut of startups. In reality, though, more often than not, many of these fintech startups are beginning to co-operate or even affiliate with the same banks and financial conglomerates.
Variety of private blockchains
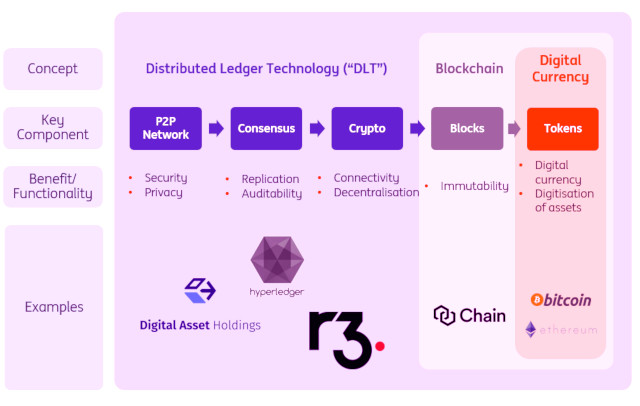
The most well-known blockchain companies in the banking sector R3, Chain, Digital Asset Holdings, Ripple, Hyperledger. Ripple is not really a blockchain project, but it has come up with a technology that could change the way money is transferred internationally through any financial institution.
R3: international commitment of 70 banks
R3 is the most famous example of a private blockchain consortium. It was created thanks to investments from banks. The R3 consortium released proprietary code for its platform called Corda on 30 November 2016. Corda has since been integrated into the open source Hyperledger project.
The main goal of R3, which has only been working on this technology for a year, is to develop a blockchain that enables the creation and deployment of smart contracts between financial institutions. Another important task is to explore new apps in trade finance, digital identity, and digital asset exchange.
The R3 team consists of highly skilled professionals who realise that there are still significant gaps in Corda. Nevertheless, they hope that through the open source community they can improve their model.
Some banks that had initially supported R3, such as Banco Santander, Goldman Sachs, or Morgan Stanley, abandoned this project without giving an explanation. R3 wanted to raise $200 million in the second round of investment from the participating banks. Some believe that the team’s demand to preserve 40% of the company prompted these banks not to participate.
Chain
Chain is a San Francisco-based company that released its code one month ago. The network is supported by 9 banks and payment companies. Its private blockchain is designed for the applications with a large volume of transactions. The target investors of Chain were mainly institutional investors and venture companies. In three different rounds of funding, Chain received $43.7 million.
Digital Asset Holdings
Digital Asset Holdings is a company invested by banks and venture companies. It intends to focus its technological efforts on capital markets and stock exchanges, to improve the systems of compensation and settlement of financial products. Its CEO is a well-known investment banker and former employee of JP Morgan. He also participated in the establishment of Credit Default Swap. Digital Asset Holdings received $67.2 million in two rounds of funding led by such banks as Goldman Sachs, JP Morgan, and Citibank.
Ripple
Ripple doesn’t use blockchain technology. Its goal is to develop a system that will reinvent the system of remittance and international transfers, as well as the disintermediated companies, such as SWIFT with its technology. Ripple obtained $93.6 million in the consistent rounds of funding, covered by banks and venture companies.
Hyperledger
Hyperledger is one of the most favourable projects for the creation of private blockchains without a particular industrial direction. This project, which involves numerous technology and consulting companies from around the world, is headed by Linux Foundation and managed as an open-source project.
Business model of private blockchains
The business model of all these initiatives lies in creating a future standard for the appropriate areas. From developing and extending these private protocols, they could become business models on which the entire field would operate in the future. Financial and banking sectors set the direction for private blockchains and manage the trends that will have an impact on other fields. Among them are insurance, telecommunications, power sector, and many other fields that want to benefit from the blockchain technology.