Blockchain has especially demonstrated its abilities in cryptocurrency projects. Although its potential is so wide that it’s impossible to determine just how far it can go.
Continuing to develop, the technology is already branching out into all areas. Managers therefore should be aware of 5 beneficial blockchain properties: decentralization, equality, cryptography, secure storage of data, and data validity. All of them are thought to be key advantages that can be applied when implementing blockchain for business.
Table of Contents
Decentralization
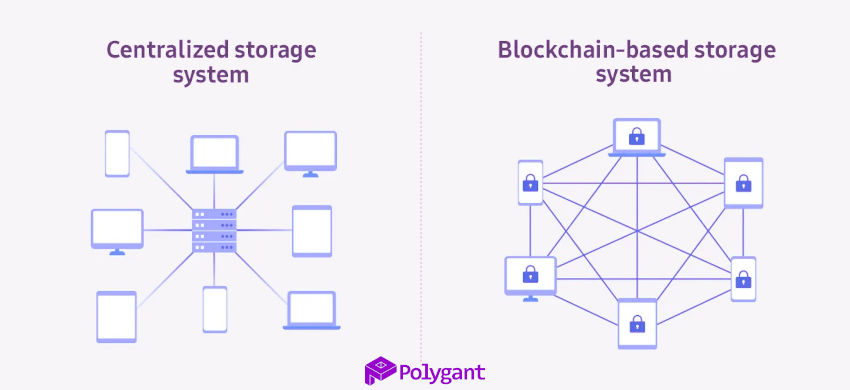
Blockchain is a distributed database that is maintained as long as at least two devices are connected to the network, behaving as a full node. Each additional computer, laptop, or tablet adds to the number of full nodes, expanding decentralization.
A full node must uphold consensus, maintain a copy of the data, and share it. The data can be the details of transactions or any type of operation, depending on the business implementing the blockchain. For a transaction to be considered valid, it must be confirmed by at least two validators.
Equality
Because all network participants possess identical copies of the blockchain, everyone has the same opportunities and privileges. In some instances, however, not everyone can become a full node or validator. This depends on blockchains, which comes in 3 types:
- Permissionless public. No permissions are required, anyone can become either a full node or a validator. Examples: Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin.
- Permissioned public. You can become a full node without permission, but the right to validate is issued by a central authority. Examples: ledgers of either corporations and government agencies that have switched to blockchains.
- Permissioned private. You can only become a full node with permission, and the central authority with its partners act as validators. Such centralized blockchains are operated by private companies.
Even in the case of the latter, validators as well as network participants should have equal rights amongst themselves. But this must be observed only within a group to a certain degree, so validators may have more rights than ordinary network participants.
Cryptography
Data in the blockchain is protected by cryptography. It ensures the privacy of the initiator of a transaction or any operation and makes it impossible to forge past records. To do this, the operation must have its own hash and reference the hash of the previous operation. And because of this, no one can either change or delete the saved records.
On public blockchains, each member of the network can view public information. At the same time, it’s impossible to identify the recipient and initiator of transactions.
The relationship between receiver and sender is secured via asymmetric cryptography. It implies that the sender uses public and private keys, and the receiver uses his/her own private key and the sender’s public key.
Secure storage of data
Data security is achieved via segmentation, encryption, duplication, and distributed storage. They are placed inside blocks, each of which is connected to the previous one, referencing its hash.
The blockchain is tamper-proof, as any change to at least one block is easily detected and rejected by the entire chain. This doesn’t mean that it can’t be hacked, at least in theory. But a hacker would have to alter so many blocks and spend so much time, effort, and money to do so, thereby making it unprofitable.
Data validity
The data recorded in the blockchain isn’t subject to change, deletion, or substitution. Attempts to do this will result in a mismatch with the hash of the previous operation or the hash of the previous block.
The authenticity and integrity of the transmitted data is confirmed via a digital signature. It is a cryptographic mechanism that can be thought of as a digital version of a handwritten signature, only with increased complexity and security. A digital signature is generated and attached to a message, contract, or transaction. It acts as evidence that the data transmitted by the sender was not tampered with on the way to the recipient.
Blockchain technology has existed for 16 years. Since then, it has been developing more rapidly and is becoming more popular every year. Thanks to these advantages, blockchain isn’t only used in finance, but in such areas as electronic document management and supply chains, as well as legal and notary services. The widespread use of technology allows us to hope that blockchain will become a useful tool in any business.